Terraspace Cloud vs Terraform Cloud
Both Terraform Cloud and Terraspace Cloud are optional paid managed services. Both provide Team-based permissions, History tracking, and GUI interface. What makes them different is that Terraspace Cloud is designed specifically for the Terraform Framework.
Dashboard
Both services provide a user-friendly dashboard to see what stacks have been historically deployed. In Terraspace Cloud, the deployments are called stacks, and applies are called updates:
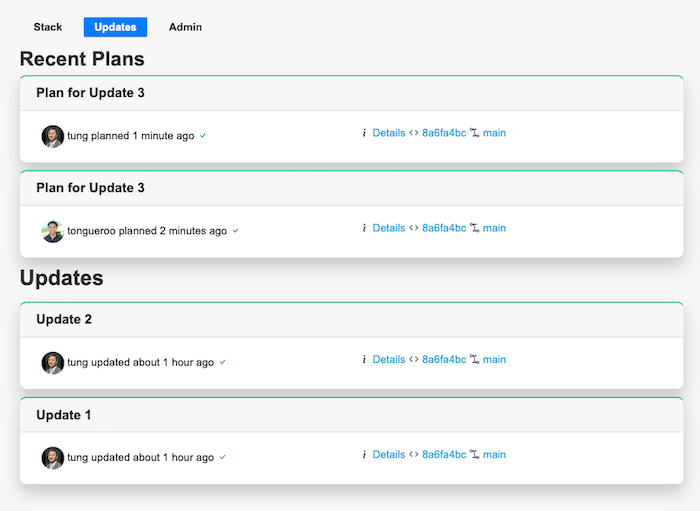
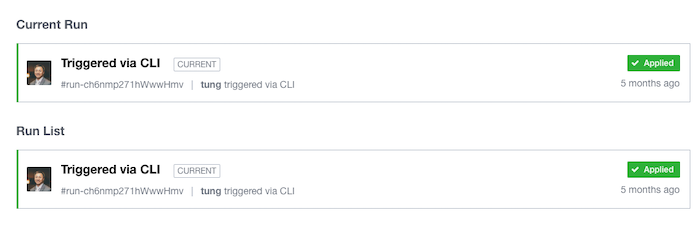
In the Terraform Cloud, deployments are called workspaces, and applies are called runs.
A difference is that with Terraspace, you don’t have to create the stack ahead of time like you have to do Terraform Cloud workspaces. With Terraspace, you can define tfvars and reference secrets with code. There’s no need to manually pre-create workspaces or stacks. They get created as you deploy.
Team Management
Both services provide a Team-based management and permissions system. Terraform Cloud permissions are focused on workspaces. Generally, admins grant permissions to teams on a per-workspace basis.
Terraspace Cloud permissions work more naturally. You define permissions and specify which projects, envs, and stacks the team will have permissions to. Terraspace Cloud Team-based permissions are more dynamic and powerful in this way. Here’s an example.
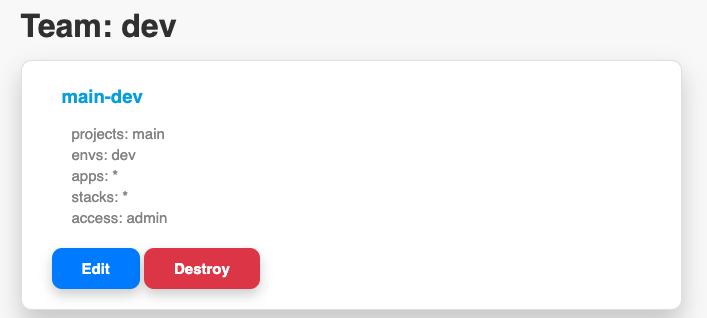
Since Terrapace provides the ability to dynamically build terraform projects and deploy them, it makes sense for a permission system with more power. The envs: dev in the permission means that users in the dev team only have access to TS_ENV=dev stacks. You can finely control the permissions based on variables. Terraspace Cloud Permissions system was explicitly designed for Terraspace.
Version Control Workflow
Terraspace also supports TFC, and you can use Terraspace directly with TFC. However, if you’re using TFC with the version control integration, you have to make sure to commit the .terraspace-cache folder and its artifacts. This is an awkward workflow but must be done since Terraform Cloud doesn’t allow you to run arbitrary commands like terraspace up.
With TSC, Terraspace is naturally integrated with the way Terraspace Cloud works. You do not have to commit any artifacts into your version control, you commit pure and clean source code. Your CI/CD process calls terraspace up directly. Docs: CI/CD.
CI/CD
Terraform Cloud provides remote runners to run your terraform apply. With Terraspace Cloud, you bring your own runner or CI systems to the table. Terraspace helps you integrate with CI systems like GitHub Actions, GitLab Pipelines, etc. This is the same approach Pulumi takes to CI/CD.
Since you bring your own machine with Terraspace Cloud, you have full control over the system. You can add your own cost analysis tool, or compliance framework as you wish. It is also faster, especially when developing from your machine. You do not have to wait for the overhead of a new VM machine to spin up for every small change. Terraspace Cloud records the plans and updates.
Backend State Control
You can keep state with your current backend. All you do is enable terraspace config.cloud settings, run terraspace up, and you’re using Teraspace Cloud. There’s zero work to migrate things like moving the backend state from s3 to the TFC remote backend.
Summary
Though Terraform Cloud and Terraspace Cloud seem similar, they are quite different. Terraspace Cloud works directly with the Terraspace framework. It provides extra features like Team Management, Permissions, History, and a GUI visual interface to Terraspace in a natural way.




