Push Workflow
Let’s take a look at the push workflow.
.github/workflows/push.yml
name: Push Up
on:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
run:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
env:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
AWS_REGION: us-west-2
GH_TOKEN: ${{ github.token }}
TS_ENV: dev
TS_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.TS_TOKEN }}
# INFRACOST_API_KEY: ${{ secrets.TS_TOKEN }} # needed if using cost estimation
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Install Ruby
uses: ruby/setup-ruby@v1
with:
ruby-version: 3.1
bundler-cache: true # runs 'bundle install' and caches installed gems automatically
- name: Install
run:
.github/bin/install
- name: Terraspace Command
run: |
terraspace up demo -y
Supporting Script
The install script installs Terraform, Terraspace, and infracost. It looks something like this.
.github/bin/install
#!/bin/bash
# install terraform
brew install tfenv
tfenv install 1.5.5 # do not use later than 1.5.5
tfenv use 1.5.5
terraform --version
# install terraspace
bundle install
bundle exec terraspace new shim
terraspace --version
# install infracost https://www.infracost.io/docs/
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/infracost/infracost/master/scripts/install.sh | sh
Environment Variables
We should set these environment variables. Note that the AWS variables are required only if you’re using terraspace_plugin_aws.
-
AWS Variables: The workflow is environment configured with
AWS_*variables, so the CI machine has permissions to create resources on AWS. The AWS token need these minimal permissions. -
GH_TOKEN: This token is grabbed from the GitHub Actions env itself via
github.token. This allows Terraspace post PR comments with a summary of the changes and cost estimates. The GitHub Actions token should have necessary permissions. If you choose to use create and use your own token, it should have “repo” permissions so it can create the PR comment.
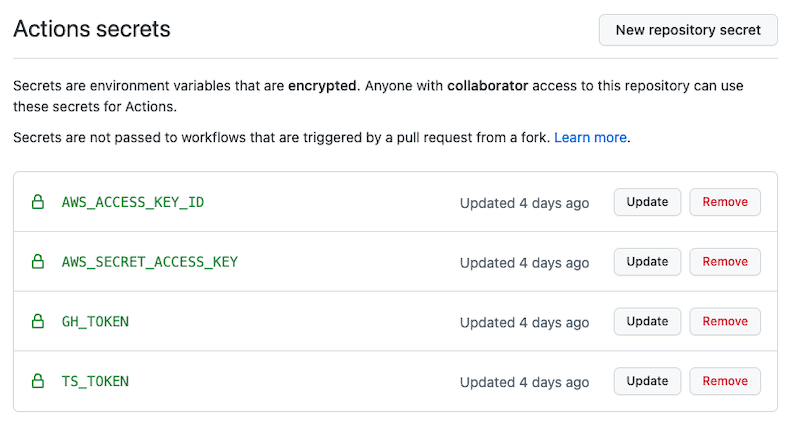
With GitHub, you have to configure these secrets before running the workflow.
- Go to the Repo Settings. It’s the tab on the right-hand side. You must own the repo or have admin permissions to see it.
- On the left-hand menu, go to Secrets / Actions.
- Click on the New repository secret
- Create the secrets, IE:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY,AWS_REGION,GH_TOKEN, andTS_TOKEN, etc.
Terraspace Command
At the very end, the terraspace up demo -y command will run to deploy the demo stack. You can customize this command or add additional commands. IE: You probably want to use terraspace all up if you prefer.
Commit and Push
Let’s commit and push the files.
git add .
git commit -m 'add ci'
git push -u origin main
This starts the build process immediately.
Results
After the job starts, you’ll see something like the following. You may have to refresh to see the job running.
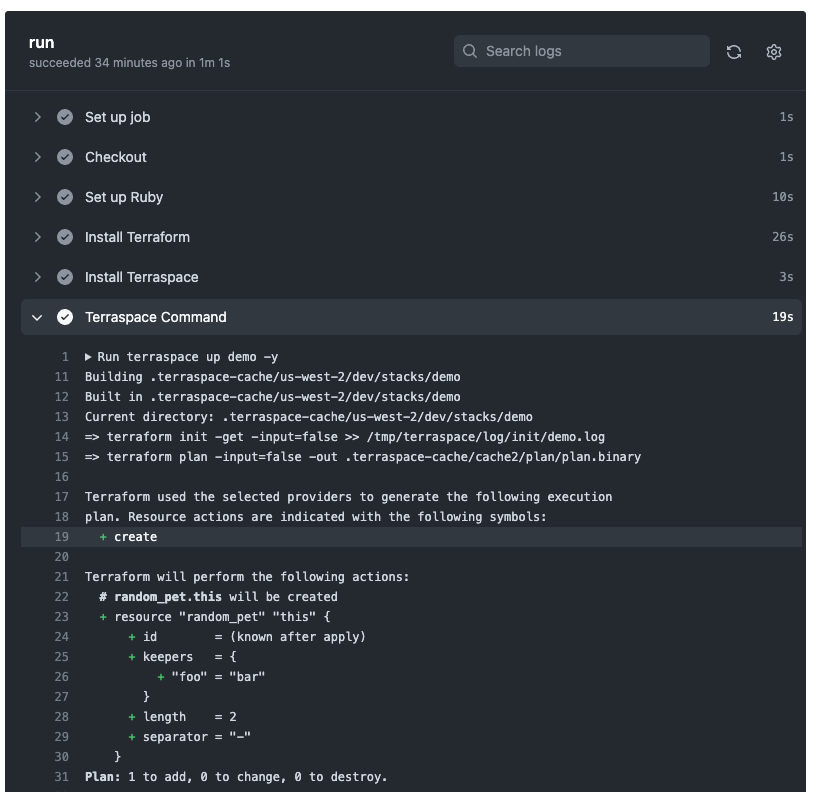
You can see that a resource was created.
Next, we’ll look at the Pull Request Workflow.





